Background
The global plastic waste production continues to accelerate at an alarming rate causing grave environmental impact. The need for degradable/recyclable plastics becomes ever more urgent. Most post-consumer plastic waste are not recycled, and are leaked into the environment or end up in landfill. Dynamic covalent polymers are an active area of research to develop polymers capable of chemical recycling to monomers (CRM), where plastic materials can be transformed back to monomers to be purified and repolymerized creating a circular economy.
Description
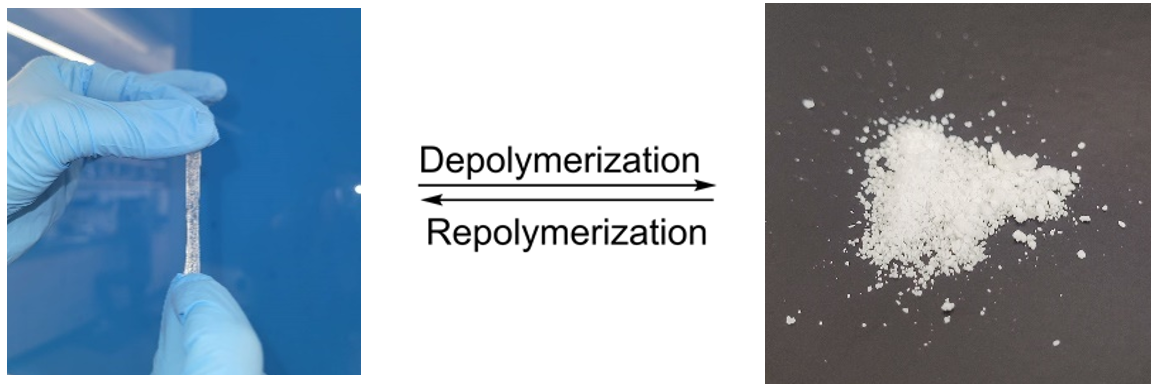
This technology involves synthesizing polydithioacetals (PDTAs) using a benzaldehyde derivative and a set of straight-chain aliphatic dithiols in the presence of an acid catalyst. Acid-catalyzed ring-closing depolymerization (RCD) of PDTAs yields a mixture of cyclic dithioacetals of various ring sizes. The entropically driven ring-opening polymerization (ROP) of these macrocyclic monomers affords the PDTAs at room temperature with high conversions. The efficient ring-chain recycling nature and tunability make PDTAs a sustainable and recyclable polymer solution.
Advantages
- Synthesis is simple. Polymer is chemically and physically stable.
- Starting materials are readily available chemicals.
- Depolymerization is conducted at elevated temperature in an organic solvent.
- Degraded product is a stable solid which is easy to store and transport.
- Minimal side product involved in the recycle process
- Tunable rates and efficiency of the polymerization process through structural variations in the polymer backbone and benzaldehyde derivatives, allowing greater control over material properties.
Potential Applications
- Packaging materials for consumer goods
- Automotive components for lightweight and durable parts
- Textiles and fibers in clothing and upholstery
- Building and construction materials, such as insulation and piping
- Electronic components, including casings and insulation materials
- Medical devices and implants with biocompatibility and reduced environmental impact
Related Patent and Publication
- Patent pending
- Dithioacetal Polymers Capable of Chemical Recycling to Macrocyclic Monomers and Formation of Vitrimers (Link)